PROJECT -> May be Bespoke/Custom/COTS (Commercial of the Shell)
PRODUCT: Developed based on manufacturer’s Specification and used by multiple/many users.
PROJECT: Developed based on Customer’s Specification and used by particular Customers.
S/W Process: The set of activities whose goal is to develop a application or Evaluation of Software.

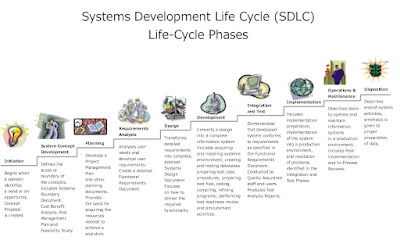
PHASES & ROLES
1. REQUIREMENT PHASE -- >
Role: Business Analyst (CRS/BRS->Customer/Business Requirement Specifications)
KICK- OFF MEETING
Project Manager sends initiation note to CEO.
TASK OF THE ENGAGEMENT MANAGER
i. Deals with the excess cost of the project.
ii. Responsible for Prototype demonstration
Protype - It is roughly & rapidly developed model.
Input Document-> BRS
2.ANALYSIS -- >
Role: System Analyst/Project Manager/Team managers.
TASK:
FEASIBILITY STUDY:
A Detailed study of requirements in order to check whether they are feasible or not.
TENTATIVE PLANNING:
The Resources as well as time temporarily planned. (Fixing Target date to accomplish project)
TECHNOLOGY SELCTION:
What are all the technologies that are required for accomplish given project successfully.
REQUIREMET ANALYSIS:
The Requirements that are required to accomplish the project successfully.
Output SRS/FRS Document (System/Functions Requirement Specification). This document contains functional requirements to be developed and system requirements to be used)
What makes a Good SRS?
Environment of S/W
Project requirements in SRS
Protyping Demonstration
Characteristics/ Features of SRS:
1. Independent
2. Easy to Validate
3. Verifiable
4. Complete
5. Consistent
6. Traceable
7. Modifiable
3. DESIGN
Role: Chief Architect/ Technical Lead
They convert all the requirements into well defined Modules.
TASK
They are doing this design in 2 ways:
1. HLD – High level Design (The overall view of S/w from root functionality to leaf functionality.)
The Process of dividing modules usually done by Chief Architect.
This design is also called as “EXTERNAL DESIGN/ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN”.
2. LLD – Low level Design
The Process of dividing modules into sub-modules in order to check internal logic of each program structure. This is usually done by Technical Lead’s
This design is also called as “INTERNAL DESIGN/DETAILED DESIGN”.
It contains some data flow diagrams and Psuedo Code.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_flow_diagram
Output TDD (Technical Design Document)
TDD->Flow Diagrams + Psuedo Code
4. CODING/DEVELOPMENT/IMPLEMENTAION-
Role: Developers
TASK:
The Programmers/Developers write coding with respect to customer specified technology.
Developers are using pseudo code & following coding standards, proper indentation(Eg. Alignments while designing web page username/pwd field.) And color coding etc..
Output Source code Document/Application
5. TESTING
Role: Test Engineers/Testers
TASK:
The testers detecting the defects from the application.
Process:
Prepare the Review Report
After understanding all the requirements clearly testers take test case template and write test cases.
After receiving a s/w build or application from developers. Testers will execute all the test cases on that application.
If they find any defects, they will report to the developer. After receiving modified build, then again testers will check for side effects. This method will repeats/continues till defect free product comes.
Output Application or Quality Product
6. RELEASE & MAINTENANCE
Role: Deployment Engineer/Senior Test Engineer
TASK:
Release the software to customer.
Process:
The Deployment engineer will display the application into the client environment following the guide lines given in the deployment document.
Maintenance
After releasing S/W, if at all any problem during the utilization of S/W, then that problem become a task for maintenance team.
Depending upon that problem the corresponding team/role will be appointed and he defines the process based on the issue and resolves it.